Planet Earth
Planet Earth: Components and Characteristics.
The Earth is one of the inner planets in the Solar System. It is the biggest rocky planet, although it is much smaller than the gaseous planets. Its equatorial radius is 63718.1km long and its estimated mass is 5.792x1024kg.
It is located between Venus (its closest planet) and Mars, and it is, on average, 150000000km from the Sun. It has an atmosphere rich in nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour.
The distance from the Sun and the atmospheric density of the planet lead to an average temperature of 15°C, from -90°C in the coldest regions to 60°C in the warmest ones, providing the optimal conditions to support life.
Planet Earth has three components:
- Atmosphere.
- Hydrosphere.
- Geosphere.
- Biosphere.
As we have just studied, the Earth’s atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the planet and it is rich in nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapour. Oxygen is very important for living beings, because they use it to respirate. Carbon dioxide is vital for plants and other autotrophic organisms, because it is necessary to carry out photosynthesis.
Atmosphere is, besides, essential to regulate the Earth’s temperature.
The hydrosphere is the layer of water that covers the Earth surface. The average temperature and its variations allow the presence of water in the three different states. 70% of Earth's surface is covered by liquid water, but we can also find significant amounts of solid water (ice) in the poles and some gaseous water in the atmosphere (water vapour).
The water of the planet can change from one state to another: liquid water can solidify when it is very cold forming solid water, or evaporate in hot places forming water vapour, for instance. This process is called water cycle.
The geosphere is the solid part of the planet. Its surface is mainly made of silicates. The most abundant component of the core is, however, iron. The movement of the iron in the core generates the Earth's magnetic field. This magnetic field is the main component of the Van Halen Belt, that protects the planet against dangerous radiation from the outer space.
Another important characteristic of the geosphere is the volcanic and seismic activity. It is related to the tectonic plates, that are dynamic components of the Earth's crust. The dynamism of the tectonic plates is responsible for changes in the Earth's surface, such as crust creation and destruction, mountain building, movement of continents and geological phenomena like volcanoes and eruptions, earthquakes or rifts.
Finally, the biosphere is made up of the living things of the planet.
Finally, the biosphere is made up of the living things of the planet.
Earth Movements
Planet Earth is not an static structure, it is moving in space. It has two basic movements: rotation and revolution.
Rotation is the spin movement of the Earth on its own axis.
Revolution also called orbit, is the movement of the planet around the Sun.
Rotation
The Earth spins on its axis. It rotates from the west to the East. The planet takes 24 hours to complete one rotation. When it is day on the half of the Earth facing the Sun, it is night on the opposite side.
The rotation axis is not perpendicular to the geographic equator, but is 23.5° tilted. Due to this, the incidence of the Solar rays that reach the planet is different in different regions of the planet and different moments of the year, depending on the part that is directly facing the Sun. This phenomena is related to the seasons and the duration of nights and days.
On the one hand, when the inclination angle makes the northern hemisphere directly face the Sun, the temperatures in this hemisphere are higher and the days are longer. We are talking about the summer in the norther hemisphere. At the same time, the temperatures in the Southern Hemisphere are lower and the days are shorter. We are talking about the winter in the Southern Hemisphere. As we can see, when it is summer in the northern hemisphere it is winter in the Southern Hemisphere.
When the inclination is maximum and the day is longest and the night shortest, we talk about summer solstice in the northern hemisphere and winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. It happens the 21st of June.
On the other hand, when the inclination angle makes the Southern Hemisphere directly face the Sun, the temperature in this hemisphere is higher and the days are longer. We are talking about the summer in the southern hemisphere. At the same time, the temperatures in the northern Hemisphere are lower and the days are shorter. We are talking about the summer in the Southern Hemisphere and the winter in the northern Hemisphere.
When the inclination is maximum and the day is longest and the night shortest, we talk about summer solstice in the southern hemisphere and winter solstice in the northern Hemisphere. It happens on the 22nd of December.
Summing up, during the summer in the northern hemisphere, this part of the Earth is exposed to more direct sunlight because this hemisphere faces the Sun. That is why the days are longer than nights. During the winter in the northern hemisphere, this part of the Earth is exposed to less direct sunlight because the rays reach the earth more transversely.
When the inclination angle is perpendicular to the incident rays day and night last just the same, twelve hours. This occurs in autumn and spring. We are talking about autumn or spring equinox. It happens on the 21st of March and the 22nd of September.
Orbit (Revolution)
Orbit is the movement of the planet around the Sun. The Earth moves around the Sun in a plane called ecliptic plane. It takes 365.25 days to complete a revolution around the Sun.
This orbit is not circular, but elliptical, so the distance between the Sun and the Earth changes. The point where the Earth is closest to the Sun is called perihelion. It happens during the northern winter, the 3rd of January. The point where the Earth is furthest to the Sun is called aphelion. It happens during the northern summer, the 4th of July.
Moon
The Moon is the Earth's natural satellite. It is much smaller than the Earth, although it is the fifth larger satellite in the Solar System, and the largest one in relation to the planet it orbits. Its equatorial radius is 1737.1km long (0.273 Earths) and it weighs 7.324x1022kg (0.012 Earths). Its atmosphere is extremely tenuous (we could nearly say that it doesn't has an atmosphere).
It is, by far, the closest relevant celestial body, and the brightest one at night.
The Moon has two movements, rotation on its axis and revolution around the Earth.
Rotation
The Moon rotates on its axis. It takes 28 eight days to complete a rotation, just the same it takes to complete a revolution around the Earth. As a result, the Moon always presents the same side to the Earth. This phenomena, called tidally locked rotation, is a consequence of the gravitational force of the Earth.
Revolution
The Moon revolves around the Earth, in an anticlockwise direction. As we have studied, it takes 28 days to complete a revolution.
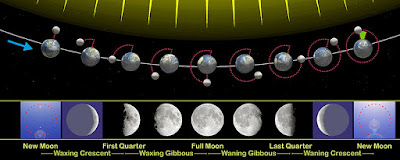
Although the Moon always presents the same face to the Earth, we only can see the part of the Moon that is reflecting the sunlight. The shape of the illumination portion of the Moon is called Lunar Phase.
The lunar phase depends on the position of the Moon in relation to the Earth and the Sun. When the sunlight illuminates the whole surface that is facing the Earth it is called a full moon. When the sunlight illuminates the opposite side of the Moon and the portion of the Moon that faces the Earth is dark, it is called a new moon.
Effects of the Moon on the Earth.
Tides
The gravitational attraction of the Moon has some relevant consequences on Earth. The most important one is the movement of sea water when attracted by the Moon, that causes tides. In the part of the Earth closest to the Moon, the sea level is slightly higher. In the opposite side of the Earth, the sea level is a also higher, because of the water movement from the lateral parts to the front. Tides are the manifestation of the sea water movement, following the Moon’s revolution.
Tides mainly lead from the gravitational attraction of the water by the Moon, but also by the Sun. Due to this, tides are higher when the Moon and the Sun are aligned with the Earth. This fact occurs with the new Moon and the full moon.
Eclipses
Eclipses occur when one celestial body projects its shadow against another celestial body, fading or obscuring it.
We can see two different types of eclipses from the Earth: Solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
Solar eclipses occur when the moon passes in front of the Sun during the day, partially hiding it and projecting its shadow to the Earth. This happens when the moon crosses the ecliptic plane of the Earth during the day, being the three celestial bodies perfectly aligned. The moon's shadow crosses the Earth, obscuring a portion of the planet.
Lunar eclipses occur when the moon crosses the ecliptic plane during the night, and it is, at the same time, perfectly aligned with the Sun. According to this, it only happens during a full moon. The Earth blocks the Sun, so it cannot illuminate the moon. Summing up, the earth's shadow obscures the moon.